C++ Programming Basic အသေးစိတ်ရှင်းပြချက်များ
Reference Book
Author – Robert Lafore
Object-Oriented Programming
Fourth Edition
C++ Programming Basics (Chapter – 2)
- Function
- Header File
- Using Cout
- Variable Name
- Comment
#include<iostream.h>
int main( )
{
cout<<“Good Morning\n”;
return 0;
}
Output is
Good Morning
1.Function
Example – main( )
int main()
{
cout<<”Hello”;
return 0;
}
main( ) ဆိုတာက function ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ ( ) ကွင်းအဖွင့်အပိတ်ပါရင် ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် function လို့ပြောနိုင်ပါတယ်။ ကွင်းအဖွင့်အပိတ် ရှေ့မှာကတော့ function name ဖြစ်ပြီး ကွင်းအဖွင့်အပိတ် နောက်မှာကတော့ function body ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ function body ကို brace လို့ခေါ်တဲ့ တွန့်ကွင်းအဖွင့်အပိတ်ထဲမှာ ရေးပါတယ်။
main = function name
main ( ) = function
{ ….. ;
….; } = function body
2. Header file
#include<iostream.h>
int main( )
{
cout<<“Good Morning\n”;
return 0;
}
အထက်က Example အရ header file က #include<iostream.h> ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ #include က header file ထည့်ရင် အသုံးပြုရတဲ့ key word ပါ။ iostream.h ဆိုတဲ့ header file ကအဓိကကျပါတယ်။ ကျန်တဲ့ header file တွေလဲရှိပါတယ်။ conio.h , math.h , iomanip.h ,….. ။ header file တွေကတော့ program အလိုက် ထည့်ရပြီး #include ကို header file တွေရှေ့မှာထည့်ပေးရပါတယ်။ ( #include<iostream.h>)
3. Using “cout” ( pronouned C out )
Cout<<”Hello! How are you. “;
( ) ဆိုရင်တော့ function ဖြစ်ပြီး braces { } ကြားမှာတော့ function body ပါ။ function body ထဲမှာ statement တွေရှိပါတယ်။ statement တွေရဲ့ နောက်မှာတော့ semicomma ” ; ” နဲ့ဆုံးပါတယ်။ အပေါ်မှာပြထားတဲ့ example ကတော့ output ထုတ်ထားတဲ့ statement တစ်ကြောင်းပါ။ cout ကို c out လို့အသံထွက်ပါတယ်။ cout က output ထုတ်ပေးတဲ့ keyword ပါ။ cout<<“……..” dot နေရာမှာရေးသမျှစာသားအားလုံးပေါ်ပါတယ်။
cout<<”Hello! How are you. “;
Output is
Hello! How are you
Run လိုက်ရင်တော့ Hello! How are you ဆိုပြီး output ထွက်လာမှာပါ။
4. Variable Names
Variable တွေကတော့ language တစ်ခုစီမှာ အရေးပါပါတယ်။ variable တစ်ခုမှာ variable name ပေးလိုက်ပြီ ဆိုတာနဲ့ variable ဟာ memory ပေါ်မှာနေရာ သွားယူပါတယ်။ ပထမကတော့ variable တွေကို define လုပ်ပေးရပါမယ်။ define လုပ်တဲ့ အခါမှာ data type လိုအပ်ပါတယ်။ integer အတွက် (int) data type, character တွေအတွက် (char) data type, ဒသမကိန်းတွေ အတွက်ဆိုရင် (float) data type ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ format က data type + variable ပါ။
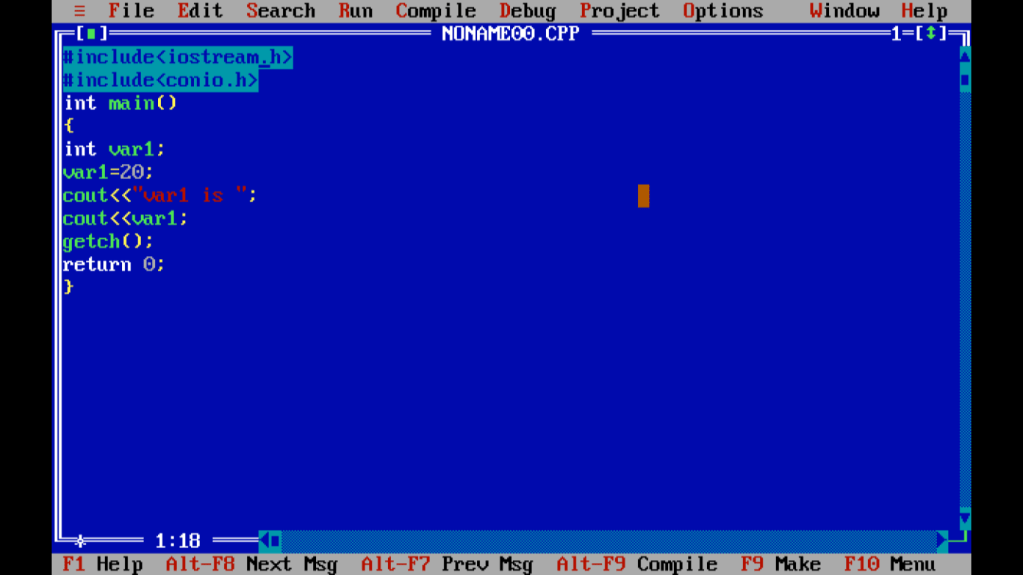
#include<iostream.h>
int main( )
{ int var1;
var1 = 20;
cout<<“var1 is “;
cout<<var1<<endl;
return 0;
}
ရှင်းပြချက်၊ ၊ <iostream.h> header file ကြေညာတယ်။ int main( ) main function ထဲမှာ statement ၅ ကြောင်း ရှိပါတယ်။ ပထမ statement မှာ int var1; variable တစ်ခုကြေညာပါတယ်။ variable name က var1 ပါ။ variable name ကို ကိုယ်ကြိုက်တာပေးလို့ရပါတယ်။ for example – a, num, no, age1 , …..etc. Second Statement က variable var1 ထဲကို integer number 20 ကိုထည့်လိုက်ပါတယ်။ int var1 မှာ variable name ရှေ့က data type က integer (int ) data type ဖြစ်တဲ့အတွက် integer number တွေဘဲ
ထည့်လို့ရပါတယ်။ Third statement က cout<<“var1 is ” Using cout မှာရှင်းပြထားတဲ့ အတိုင်း ” .. ” double code ထဲမှာ ရေးတဲ့ အတိုင်းပေါ်ပါမယ်။ cout နဲ့ output ထုတ်ထားတဲ့ အတွက် screen ပေါ်မှာ double code ကြားထဲက var1 is က screen ပေါ်မှာပေါ်ပါမယ်။ fourth Statement မှာ var1 ကို double code နဲ့မဖော်ပြတဲ့အတွက် var1 ထဲကို assign လုပ်ထားတဲ့ integer value 20 ကပဲ screen ပေါ်မှာ ပေါ်ပါမယ်။ Output ကတော့
var1 is 20 ပါ။
return0 အကြောင်းကတော့ function အပိုင်းမှာထည့်ရှင်းပြထားပါတယ်။

5. Comments
Comments တွေကလည်း အရေးကြီးပါတယ်။ တစ်ယောက်ထဲအသုံးပြုရင် အရေးမပါပေ
မယ့် group လိုက် project လုပ်မယ့်အခါ မျိုးတွေမှာအသုံး၀င်ပါတယ်။ Comment တွေက Run လိုက်ရင် screen ပေါ်မှာ မပေါ်ပါဘူး။
In symbol, // or /* */
//comment syntax //comment .cpp
//demonstrates comments
#include<iostream.h>
int main()
{
cout<<”Every age has a language of its own \n”;
return 0;
}
Output is
Every age has a language of its own
In other way
/* this is the start of comment and
you can write any text and can give any
comment to reader who read your program
this is the end of comment */
#include<iostream.h>
int main()
{
cout<<“Hello! Good Morning\n” ; //Greeting
cout<<“How are you?\n”; /* Greeting */
return 0;
}
Output is
Hello! Good Morning
How are you?
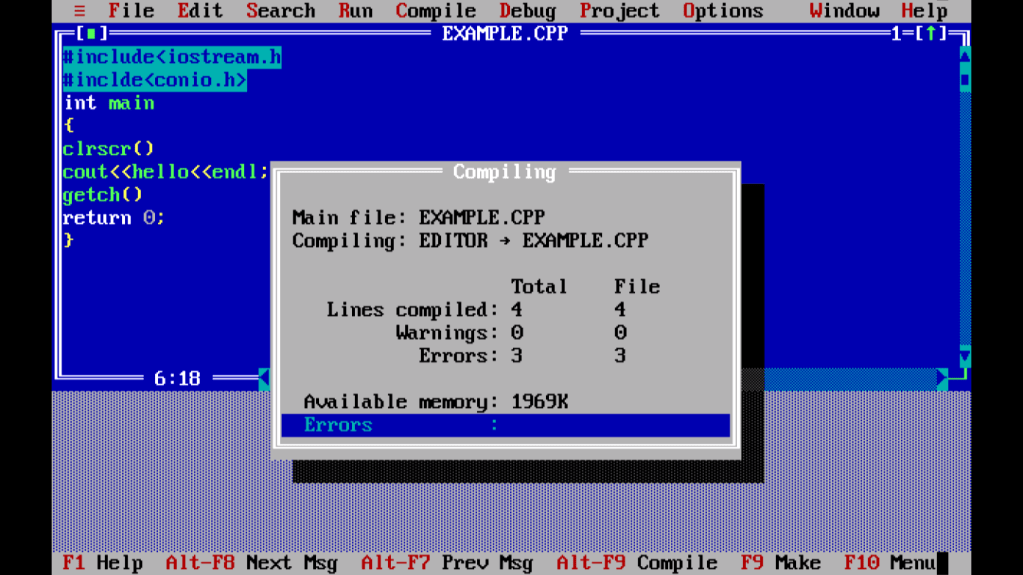
Turbo C မှာ Run မယ်ဆိုဘာတွေလိုပါသလဲ ?
- Turbo C ကို install လုပ်ပီးစစခြင်းဖွင့်လိုက်တဲ့ file က CPP file မဟုတ်ပါဘူး။ အဲ့ဒီ file မှာ coding ရေးပြီး Run လိုက်တဲ့ အခါ Run မရဖြစ်နေတတ်ပါတယ်။ အဓိက က CPP file မှာပဲ Run လို့ရတဲ့အတွက် File tab ထဲက new မှာ file အသစ်ဖွင့်ရပါမယ်။ Extension name က CPP ပါ။
- အပေါ်မှာပြထားတဲ့ example program တွေမှာ မပါမဖြစ် function နှစ်ခုလိုပါသေးတယ်။ clrscr function နဲ့ getch function ပါ။ clrscr function ကတော့ clear screen ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ clear screen မလုပ်ရင်တော့ ရှေ့က run ထားတဲ့ program က Run ထားတာတွေပါတွဲပြီး Output ထုတ်ပြမှာဖြစ်ပါတယ်။နောက်တစ်ခု က getch( ) function ပါ။ clrscr( ) ကို main( ) function body အစမှာထည့်ပေးရပြီး getch function ကို main function body အဆုံးမှာထည့်ပေးရပါတယ်။
- C++ မှာ ကိုယ်ရေးတဲ့ program အတွက် Header file ( include file ) တွေကိုလိုသလိုထည့်ပေးရပါတယ်။ အပေါ်မှာဖော်ပြထားတဲ့ clrscr( ) နဲ့ getch ( ) function အတွက် လိုအပ်တဲ့ Header file က (CONIO) ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ #include<conio.h> ဆိုပြီး header file ထည့်ပေးရမှာပါ။
#include<iostream.h>#include<conio.h>int main( ){clrscr();cout<<“Good Morning\n”;getch();return 0;}
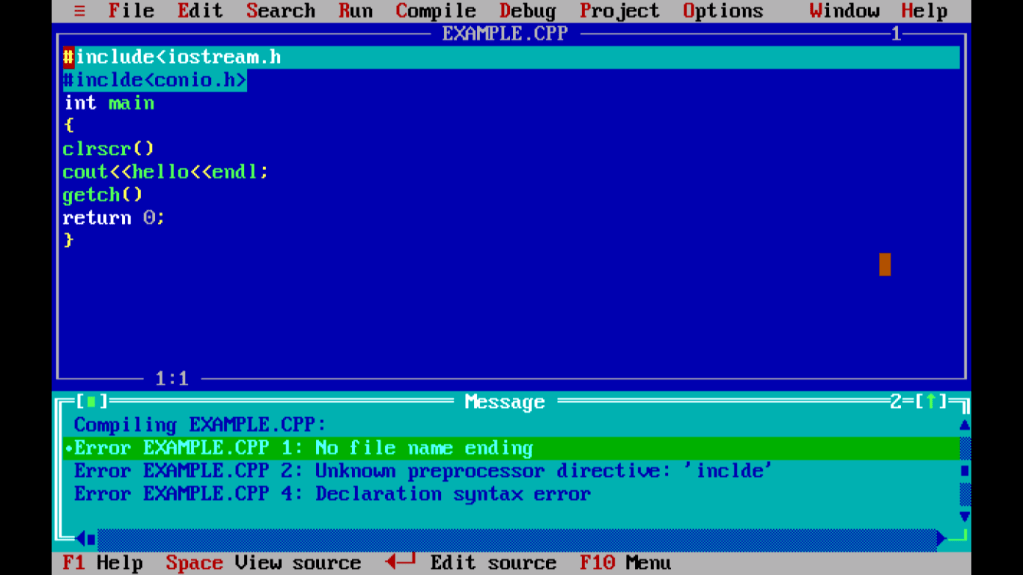
- နောက်တစ်ခုက Error ကိစ္စပါ။Statement တွေရဲ့ နောက်မှာ semicolon လိုနေတာတွေ, စာလုံးပေါင်းမှားနေတာတွေကတော့ Error Message မှာ line number နဲ့ပြီးဖော်ပြတဲ့အတွက် Errors တွေကိုကြောက်စရာမလိုပါဘူး။