Chapter-5
no.1
Refer to the CIRCAREA program in Chapter 2, “C++ Programming Basics. ” Write a function called circarea( ) that finds the area of a circle in a similar way. It should take an argument of type float and return an argument of the same type. Write a main( ) function that gets a radius value from the user, calls circarea ( ) , and displays the result.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
float circarea(float); //function declaration
int main()
{
clrscr();
float r,ans;
cout<<“Enter the radius of a circle: “;
cin>>r;
ans=circarea(r); //function call
cout<<“\nThe area of a circle is: “<<ans;
getch();
return 0;
}
float circarea(float rads) //function defination
{
float area;
area=3.14 * (rads*rads);
return area;
}
Output is

no.3
Write a function called zeroSmaller( ) that is passed two int arguments by reference and then sets the smaller of the two numbers to 0. Write a main( ) program to exercise this function.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void zerosmaller(int&, int&); //function declaration
int main()
{
clrscr();
int x,y;
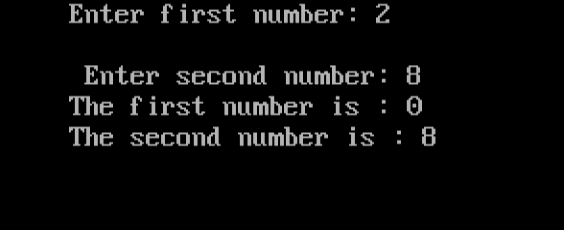
cout<<“Enter first number: “;
cin>>x;
cout<<“\n Enter second number: “;
cin>>y;
zerosmaller(x,y); //function call
cout<<“The first number is : “<<x;
cout<<“\nThe second number is : “<<y;
getch();
return 0;
}
void zerosmaller(int &x,int &y)
{
int temp;
if(x<y)
x=0;
else
y=0;
}
Output is
no.4
Write a function that takes two Distance values as arguments and returns the larger one. Include a main( ) program that accepts two Distance values from the user, compares them, and displays the larger.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int larger(int, int); //function declaration
int main()
{
clrscr();
int f,s,large;
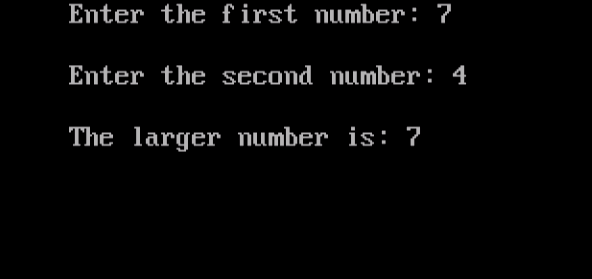
cout<<“Enter the first number: “;
cin>>f;
cout<<“\nEnter the second number: “;
cin>>s;
large=larger(f,s); //function call
cout<<“\nThe larger number is: “<<large;
getch();
return 0;
}
int larger(int x, int y) //function defination
{
if(x>y)
return x;
else
return y;
}
Output is
no.5
Write a function called hms_ to_secs( ) that takes three int values_ for hours, minutes, and seconds _ as arguments and returns the equivalent time in seconds (type long). Create a program that exercises this function by repeatedly obtaining a time value in hours, minutes
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
long hms_to_secs(int, int, int); //function declaration
int main()
{
clrscr();
int h,m,s;
char ch;
long totalsec;
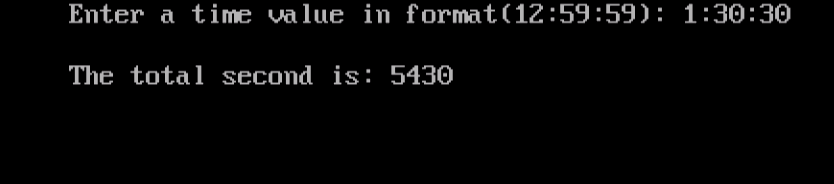
cout<<“Enter a time value in format(12:59:59): “;
cin>>h>>ch>>m>>ch>>s;
totalsec=hms_to_secs(h,m,s); //function call
cout<<“\nThe total second is: “<<totalsec;
getch();
return 0;
}
long hms_to_secs( int h ,int m , int s ) //function defination
{
long ans;
ans=(h*3600)+(m*60)+s;
return ans;
}
Output is
no.6
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
struct time
{
int h;
int m;
int s;
};
long time_to_secs(time ,time); //function declaration
void secs_to_time(long); //function declaration
int main()
{
clrscr();
time t1,t2;
char ch;
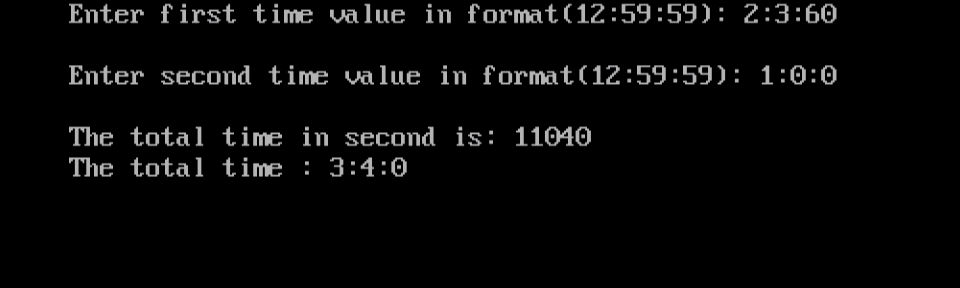
cout<<“Enter first time value in format(12:59:59): “; cin>>t1.h>>ch>>t1.m>>ch>>t1.s;
cout<<“\nEnter second time value in format(12:59:59): “; cin>>t2.h>>ch>>t2.m>>ch>>t2.s;
long ans=time_to_secs(t1,t2); //function call
secs_to_time(ans);
getch();
return 0;
}
long time_to_secs(time t1,time t2) //function defination
{
long total_t1_secs, total_t2_secs, total_secs;
total_t1_secs=(t1.h*3600)+(t1.m*60)+t1.s;
total_t2_secs=(t2.h*3600)+(t2.m*60)+t2.s;
total_secs=total_t1_secs+total_t2_secs;
return total_secs;
}
void secs_to_time(long s) //function defination
{
int ans_h=s/3600;
int ans_m=(s%3600)/60;
int ans_s=(s%3600)%60;
cout<<“\nThe total time : “<<ans_h<<‘:'<<ans_m<<‘:'<<ans_s;
}
Output is